SOLUTIONS & PRODUCTS
Products



BUY | QUOTE
BUY | QUOTE
English
International



BUY | QUOTE








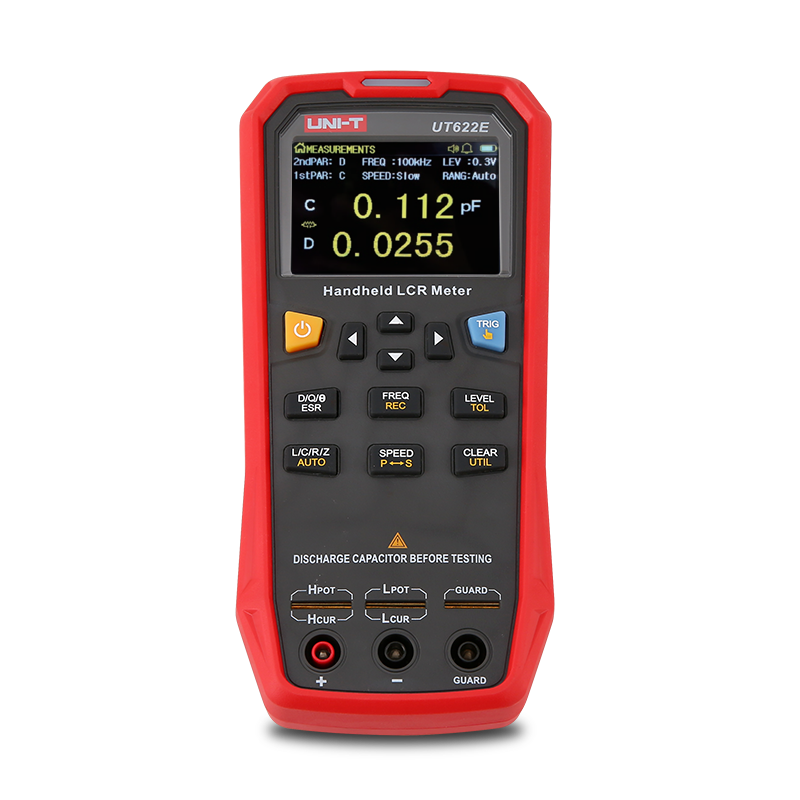
The quality factor Q of an inductor indicates the degree to which the device approaches a pure reactance. A higher Q value indicates a larger absolute value of reactance, a smaller series resistance, and lower energy loss.
For capacitors, the purity is usually represented by the dissipation factor D, where D = 1/Q. Therefore, a smaller D value corresponds to a larger capacitive reactance and better efficiency.
The quality factor Q of an inductor indicates how close the device approaches pure reactance; the larger the quality factor, the greater the absolute value of the reactance.
For capacitor, this item indicating purity is usually expressed by the dissipation factor D, D=1/Q; therefore the smaller the D, the higher the capacitive reactance and the better the efficiency.
Has short circuit and open circuit zeroing been performed?
Confirm that short-circuit (for resistance) and open-circuit (for capacitance and inductance) compensation procedures have been correctly performed before testing.
Is the device under test a known standard source?
Ensure that the component being measured is a calibrated standard or a known reference. Using uncalibrated or damaged components as references can lead to inaccurate assumptions about error.
Is the range set to AUTO?
Check if the meter is set to AUTO range mode. In some cases, manually selecting the correct measurement range improves accuracy and stability.
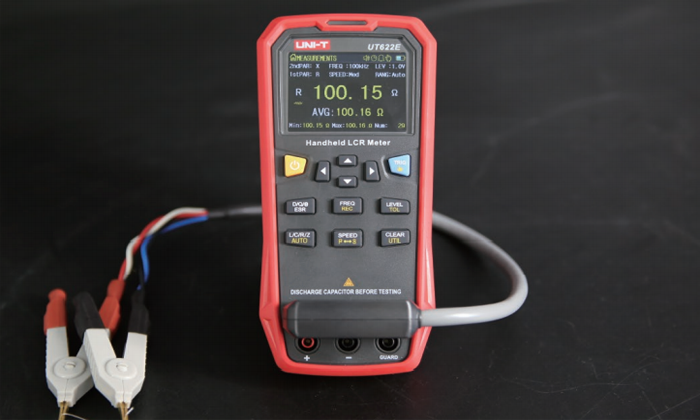
DCR refers to the direct current resistance measurement mode.
It can measure the direct current impedance of electronic components such as coils and transformers.
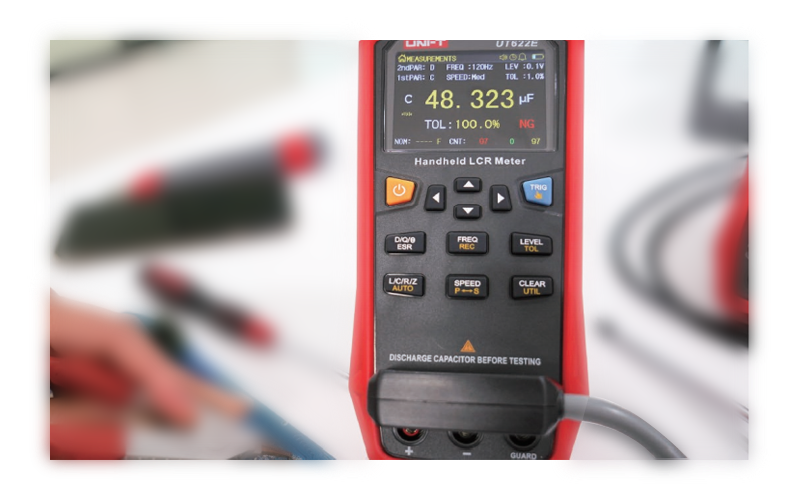
1. There was a reverse connection during the testing of the test clip
2. The testing frequency is too high (the fundamental frequency of the electrolytic capacitor is as low as 120Hz or 1Khz)
3. Select test mode: electrolytic capacitors are suitable for parallel connection Cp




